Splicing Proofreading at 5' Splice Sites by ATPase Prp28p
Splicing fidelity is an important issue due to the accuracy and flexibility must be addressed for the intron consensus sequences during pre-mRNA splicing. Although it has been reported that several ATPases modulate splicing fidelity at different stages of splicing, however, it is still not clear how the accuracy in 5' splice site (SS) selection is attained and whether the ATPase Prp28p is involved.
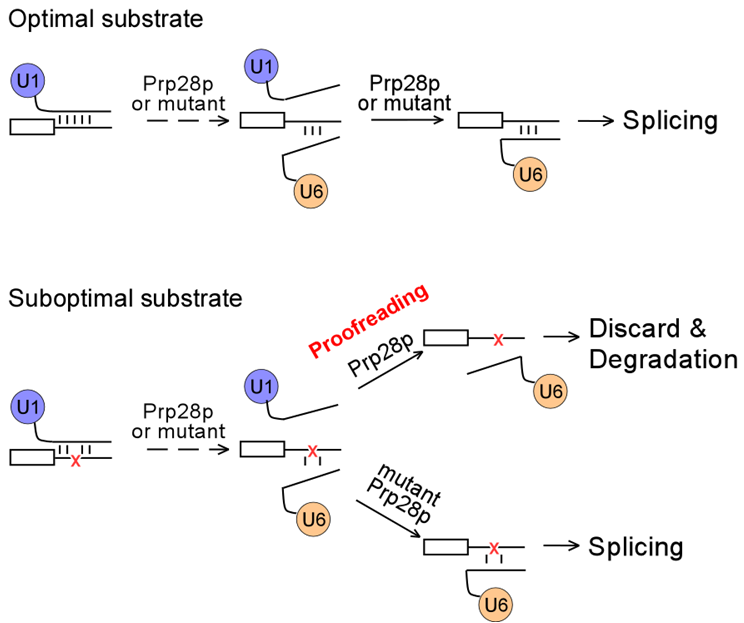
Group from the Institute of Plant Physiology and Ecology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, CAS, led by Prof. Yong-Zhen Xu, provides evidence that the spliceosomal ATPase Prp28p proofreads splicing at 5' splice sites. They have used a series of yeast genetic screens to obtain prp28 alleles that specifically alter splicing of suboptimal 5'SS substrates. Prp28p is thought to facilitate the disruption of 5'SS–U1 snRNA pairing to allow for 5'SS–U6 snRNA pairing in the catalytic spliceosome. Unexpectedly, the Prp28p-mediated proofreading is dependent upon the stability of the 5'SS:U6 duplex, but not the 5'SS:U1 duplex. Movement of the 5'SS across U6 snRNA by Prp28p competes with the stability of the 5'SS:U6 duplex, resulting in rejection of weak 5'SS–U6 pairs. However, the slowed activity of mutant prp28 alleles would allow more time for the association of a weakened 5'SS:U6 duplex, thereafter progressing to allow an improved first step of splicing. They also demonstrated that a linker region between the ATPase subdomains in Prp28p plays important roles in splicing efficiency across species as well as proofreading of 5'SS.
Entitled “Splicing proofreading at 5' splice sites by ATPase Prp28p”, this research was published online in the Nucleic Acids Research on March 5, 2013. This work was carried out by graduate student Fei Yang and colleagues, under the supervision of Prof. Yong-Zhen Xu, and supported by grants from the CAS, NSFC and the National Basic Research Program of China.
Prp28p proofreads splicing at 5'SS during the association of 5'SS with U6 snRNA. (Image provided by Yong-Zhen Xu’s group)